Electric cars bring with them many advantages. They are more sustainable, more environmentally friendly and more economical than petrol or diesel. But of course there are not only obvious advantages, but also the other side. For many, the long charging time and the short range despite a fully charged battery are a drawback. If you don't have a charging station in front of your door and often drive long distances in particular, you have to calculate very precisely how far the e-car will travel. But with the installation of your own wallbox, you can charge quite conveniently at home. Read here why a wallbox is preferable to a usual socket, which should only be a stopgap solution, and what other factors generally affect the charging process.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Comparison of e-car charging times depending on charging stations
- AC charging stations
- DC charging pole
- Household socket
- Wallbox
- Influencing factor vehicle model
- Examples of current models (overview table)
- Other factors influencing the charging time for e-cars
- Outdoor temperature
- Battery charge level
- Connector types
- Comparison of normal and fast charging (advantages and disadvantages)
- Comparison of household socket and wallbox
- Charging costs
- Conclusion
COMPARISON OF CHARGING TIME FOR E-CAR IN DEPENDENCE OF THE CHARGING STATION
The charging time of your electric car can vary extremely depending on the charging station. It is best to always be aware of when your e-car needs to be ready for use so that you remain mobile. If necessary, always plan a little extra time for longer journeys. Although charging stations can now be found in more and more places in public spaces and offer the possibility, there are also great differences here.
AC charging stations
The average charging station charges your e-car with alternating current (AC). Every electric car on the market is suitable for this type of charging. So-called on-board chargers in the vehicle convert the alternating current into direct current. However, there are already differences in the type of charger installed. You also need the right charging cable and a charging card or the app of the respective provider of the charging point. The charging power here varies between 3.7 (for comparison: a household socket provides a maximum of this power) and 22 kilowatts. With a charging power of 11 kW, you can expect a range of 100 kilometres for your e-car after 2 hours of charging. You need approx. 2 to 4 hours to fully charge your e-car.
DC charging stations
A faster variant is offered by the fast charging stations with direct current (DC), at which it is possible to charge the e-car in one hour for a range of 250 kilometres. Here, direct current is charged directly into the battery. To be able to guarantee this, the rectifier is built into the charging pole, which ensures that the alternating current is converted into direct current. But at the moment, at least vehicles offer the technical prerequisites. Most electric vehicles have a maximum speed at which charging can take place. The Nissan Leaf e+, for example, stops at 47 kW.
Household socket
As an emergency solution, it is also possible to connect the battery to your household socket using a special charging cable. However, this charging process takes up to 14 hours and even longer before it is completed. Since the power is just 2.3 kilowatts on average. Furthermore, there is a risk that the socket will overheat during this task. For electric cars, this is therefore an absolute emergency solution that should not be used too often.
Wallbox
To avoid this overheating, the installation of a so-called wallbox is recommended. These wall charging stations are installed together with the residual current circuit breaker (type A/type B) at home or in your company by a specialist and take over the function of a plug connection for charging cables. This way, your electricity grid is not overloaded and your electric vehicle can be charged with a power of between 3.7 and 22 kilowatts in a few hours. With a charging power of 11 kW, for example, you need one hour of charging time for 100 kilometres of range. If you link your wallbox to a low-cost green electricity tariff, you will not only save time, but also money if you have a corresponding electric mileage. Please note that a wallbox with an output of more than 12 kVA requires approval from your local grid operator in addition to registration.
INFLUENCE FACTOR VEHICLE MODEL
Whether you charge your battery with alternating current or directly with direct current also depends on your vehicle model, as described above. The installed on-board charger determines whether you can charge with one, two or three phases. If your e-car is only designed for single-phase charging, the charging cable can be connected to only one strand of the available power cable. The theoretical 22 kilowatts with which the electric car can be charged are thus minimised to an average of 4.6 kilowatts of power. This is because in Germany this type of power output is limited for technical and legal reasons. This is due to the "Schieflastverordnung" (Ordinance on Unbalanced Charging) that applies in this country. If too many e-cars were to charge at full power from the grid at the same time, this could result in a power blackout.
Examples of current models (overview table)
But what exactly do the different electric car models on the market look like? We show you a comparison of some e-cars.
| Model | Battery capacity | Total range | Charging time AC charging station | Charging time Schuko | Wallbox charging time |
| Audi eQ3 | 46 kWh | 330 km | 2 h | 35 h | 4 h |
| BMW i3 (60 Ah) | 18.8 kWh | 190 km | 4,5 h | 8,5 h | 3 h |
| Citroën Berlingo Electric | 22.5 kWh | 170 km | 7,5 h | 10 h | 7 h |
| Fiat 500e | 24 kWh | 135 km | 4h | 10,5 h | 3-4 h |
| Ford Focus Electric | 33.5 kWh | 225 km | 5,5 h | 15 h | 5,5 h |
| Honda e | 33.5 kWh | 200 km | 5 h | 16 h | 7,5 h |
| Kia e-Niro | 39.2 kWh | 289 km | 5,5 h | 17 h | 8 h |
| Renault ZOE R240 | 22 kWh | 240 km | 1,75 h | 13,5 h | 7 h |
| VW ID 3 | 58 kWh | 420 km | 5,20 h | 26 h | 5,5 h |
There are big differences between the different manufacturers and also between the models as far as charging times are concerned. It is therefore essential to find out which electric vehicle model is most profitable for you and your company and which will get you up and running again the fastest.
FURTHER INFLUENCES ON CHARGING DURATION E-car
It is not only the on-board chargers and various charging options that determine the charging performance. Other influencing factors also favour or slow down the charging process of e-cars.
Outdoor temperature
The performance and capacity of the battery drop significantly when the outside temperature is below 10 degrees Celsius. When it is cold, the heating system also consumes much more energy. This has a noticeable effect on the battery power of the electric car. The vehicle lighting also needs more energy to function properly in the cold. In addition, the charging process takes much longer with a cold battery. It is therefore advisable not to charge the electric car throughout the night, if possible, so that the battery does not cool down completely. So, at best, connect it to the wallbox directly after arrival, when the battery is still warm.
As harmful as cold is, excessive heat is also unfavourable. In the long run, this damages the lithium ions in the battery. Therefore, if possible, park your electric vehicle in the shade in summer so that your battery does not age as quickly. When purchasing an electric vehicle, it is best to find out about the option of battery air conditioning, which guarantees a temperature between 15 and 25 degrees Celsius all year round.
Battery charge level
Another, not insignificant, influencing factor on the charging time of the e-car and the durability of your battery is the charge level. The golden rule here is: the battery charge should at best be between 20 and 80 percent. In this state, the energy storage unit can provide full power. The fuller the battery, the slower the charging process. If you still want to fully charge the electric vehicle to guarantee the longest possible range, you should drive off immediately after charging. Because constantly exhausting the charging capacity can also be harmful to the battery in the long run.
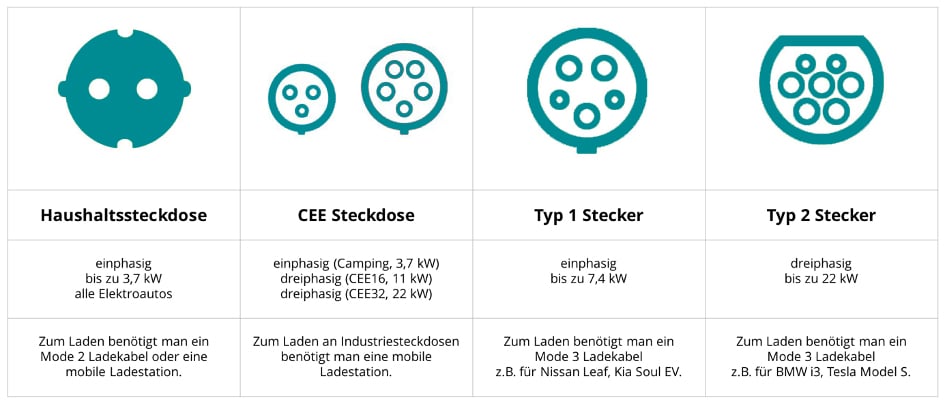
Plug type
Type 1 charging plug
This type of plug is found especially in Asian or American models. Type 1 is designed for single-phase charging and charges with a maximum power of 7.4 kilowatts. You also need a mode 3 charging cable.
Type 2 charging plug
This charging plug is designed for three-phase charging. It has a much higher power output than the Type 1 plugs. It is designed for fast charging and has an output of up to 43 kilowatts. Even at wallboxes, a charge of up to 22 kilowatts can be ensured. Here, too, you cannot do without a Mode 3 charging cable.
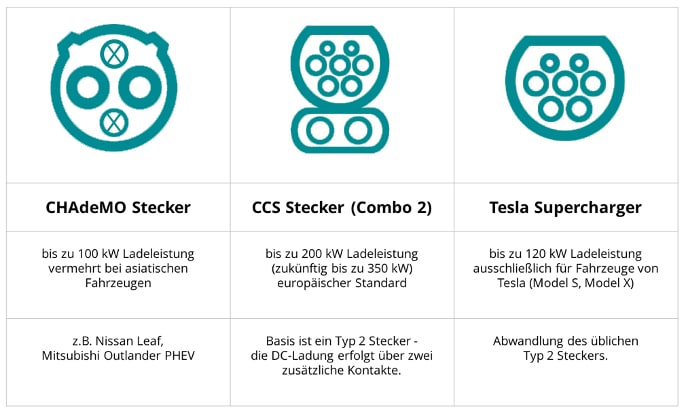
CCS plug
This is an extension of the type 2 charging plug with two additional contacts. This enables charging with both alternating and direct current. It can also be used on connections for type 2 plugs and charges with an output of 50 kilowatts.
CHAdeMO plug
The CHAdeMO plug is a Japanese fast-charging plug that theoretically charges with an output of up to 150 kilowatts. In reality, however, it also taps around 50 kilowatts of fast electricity from public charging stations.
Tesla Supercharger
This type of plug is based on the Type 2 charging plug and, according to the manufacturer, charges up to 80 per cent of the battery within half an hour with an output of 150 kilowatts. Other models have so far been denied this type of plug.
Household socket (recommended for emergency charging only)
As mentioned earlier, using a safety contact or household socket to charge your electric vehicle is not meant to be permanent. With a maximum power of 2.3 kilowatts, charging not only takes a very long time, it also puts a massive strain on your power grid. In addition, you need a Mode 2 cable and a mobile charging station.
CEE plug (not recommended as permanent application)
It used to be called a "camping plug" because it was used to charge motorhomes. In contrast to the household socket, this plug can withstand a permanent charging load. It is available in the single-phase version with up to 3.7 kilowatts of power and in the three-phase version with up to 22 kilowatts of power. Here, too, you need a mobile charging station when using an industrial socket.
NORMAL AND FAST CHARGING IN COMPARISON (ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES)
As already mentioned in the article, there are a few things to consider when charging electric vehicles. Here is a summary of all the important facts.
Normal charge:
- Saves the battery
- Risk of overheating is minimised
- AC charging points are found more frequently than DC charging points
- Vehicles with this technology are cheaper to purchase
- The house socket can serve as a charging station if necessary
- The time factor has a negative impact
- Parking spaces for e-cars are usually subject to a time limit
Quick charge:
- More innovative technology
- Faster charging
- Can be used more quickly in the public and commercial sectors
- So far, higher acquisition costs for vehicles with this technology as well as for equipment.
- Fewer charging stations available
- Electricity is more expensive
Although the advantages of normal charging outweigh the disadvantages at first glance, the time aspect should not be underestimated. This is one of the most compelling arguments, along with the lifespan of the vehicle. Moreover, fast charging is currently often slowed down by a lack of capacity in terms of charging stations. If the network is adapted in this respect in the future, there should be fewer obstacles to fast charging. For all the joy of less time spent charging, the "normal" variant, also known as snore charging, still has the advantage that it conserves the battery. Even if you drive an e-car with the appropriate technology, you should give the battery a little rest now and then.
COMPARISON OF HOUSEHOLD SOCKET AND WALLBOX
Household socket
- Charges without damaging the battery
- A "ready to hand" option in case of emergency
- No extra installations needed
- overloads their power grid
- overheats during the process
- Can lead to cable fire
Wallbox
- Simple installation
- Charging time significantly faster
- Relieves the load on your power grid
- cheaper in the long run
- Tested by experts and individually adapted
- Additional expenses due to installation
It is clear that the advantages of a wallbox clearly outweigh the disadvantages and therefore charging at such a fixed installation is strongly recommended. However, a few factors should be taken into account when purchasing a wallbox.
You should always have the installation of a wallbox carried out by electrical specialists. They are best able to assess the important aspects and take care of the necessary registration with the local grid operator. How far is your parking space from the house, do you have to dig or break through walls, which cables are already in place and do you need a stand for the wallbox. All these questions need to be clarified in advance. If it is really necessary to lay a line first, make sure that it is directly designed for 22 kW so that you do not have to retrofit it later.
Furthermore, it must be taken into account that each wallbox must have its own power circuit. This circuit must be protected by a circuit breaker and a residual current circuit breaker.
CHARGING CURRENT COSTS
Now the only question that really remains to be answered is the cost of the various charging options. There are massive differences in the price recorded here.
Wallbox - charging at home
The installation of a wallbox comes at a one-time cost of 700 to 2000 euros, depending on the effort involved. However, the investment pays off enormously. From 26.11.2020, you will receive a subsidy of 900 euros from KfW Bank for a charging station in residential properties. This is a great gain for private individuals in particular, but landlords, housing associations and of course companies also benefit from this grant. This subsidy must be applied for before the installation of a wallbox and is applicable to the installation as such as well as to the grid connection. In addition, there are particularly favourable electricity tariffs that you can use to charge your e-car. Since your wallbox draws energy via a separate circuit, there is the possibility of a very low-cost electricity tariff here. This can save you several hundred euros per year. So if you want to charge in front of your door, you should definitely do it via a wallbox.
AC and DC charging points - public charging
Depending on the region or time of day, you may pay up to 50 cents per kilowatt hour. On average, however, the costs are around 30 cents. With DC charging stations, the costs can easily rise to 80 cents. You should look in advance for the most favourable electric mobility provider with the best conditions for you.
CONCLUSION: THE WALLBOX IS THE CLEAR WINNER
It can be said that the cost factor is set against the time factor. Starting with the purchase of an electric vehicle, through electricity tariff comparisons, to the various charging options, there is a lot to consider. In the end, it all comes down to how much time you can and may allow yourself to spend charging your vehicle. However, every electric vehicle owner is recommended to install a wallbox, especially in light of the current KfW subsidies. In our comparison, they are the best solution in terms of convenience, charging time and safety.
Do you already know our comprehensive white paper? Here you will find a lot of information if you are planning to add e-cars to your fleet. Do you have any questions about CleverShuttle or a completely different